The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) had a series of ambitious missions on its horizon, spanning lunar exploration, human spaceflight, planetary research, satellite launches, and more. While developments might have occurred since then, here is a summary of ISRO’s upcoming missions and ISRO’s 4 Upcoming Missions : First one will blow your mind :
Table of Contents
ADITYA-L1
Aditya L1 will be India’s first space mission to study the Sun. The spacecraft will be placed in orbit around the Sun-Earth system’s Lagrange point 1 (L1), which is about 1.5 million km from Earth. A satellite placed in a halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously observing the Sun without any obscuration/eclipse. This will provide a greater advantage of observing solar activities and their influence on space weather in real time.
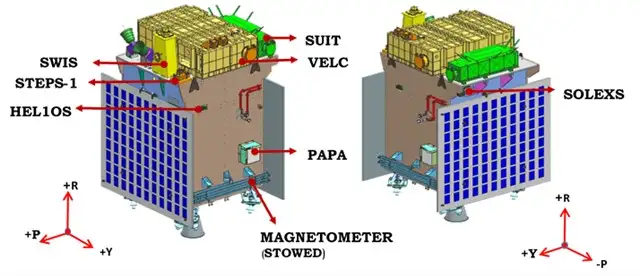
The spacecraft carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere, and outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors. Using a special L1 vantage point, four payloads directly observe the Sun, and the remaining three payloads perform in-situ studies of particles and fields at the L1 Lagrange point, providing important scientific studies of the propagation of the effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary environment.
The Aditya L1 payload suits are expected to provide the most important information to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, space weather dynamics, particle and field propagation, etc.
X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat)
XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is India’s first dedicated polarimetric mission to study the various dynamics of bright astronomical X-ray sources under extreme conditions. The spacecraft will carry two science payloads into low Earth orbit. The primary payload POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) will measure polarimetry parameters (degree and angle of polarization) in the middle X-ray energy range of 8-30 keV photons of astronomical origin. The XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) payload will provide spectroscopic information in the energy range of 0.8-15 keV.
The emission mechanism from various astronomical sources such as black holes, neutron stars, active galactic nuclei, pulsar wind nebulae, etc. originates from complex physical processes and is difficult to understand. While spectroscopic and temporal information from various space observatories provides a wealth of information, the exact nature of the emission from such sources still poses deeper challenges for astronomers.
Polarimetric measurements add two additional dimensions to our understanding, the degree of polarization and the angle of polarization, and are thus an excellent diagnostic tool for understanding emission processes from astronomical sources. Polarimetric observations together with spectroscopic measurements are expected to break the degeneracy of various theoretical models of astronomical emission processes. This would be the main thrust of research from XPoSat by the Indian scientific community.
NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) Satellite
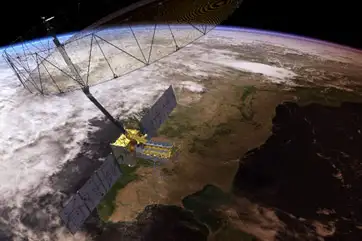
NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) is a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory jointly developed by NASA and ISRO. NISAR will map the entire globe in 12 days, providing spatially and temporally consistent data to understand changes in Earth’s ecosystems, ice mass, vegetation biomass, sea level rise, groundwater, and natural hazards including earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides.
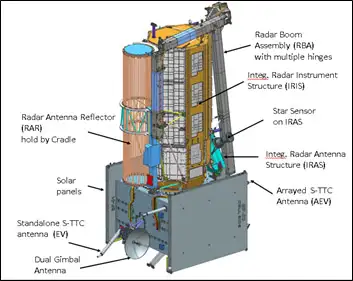
NISAR. It carries L and S dual-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) which works with Sweep SAR technique to achieve large coverage with high data resolution. The SAR payloads mounted on the Integrated Radar Instrument Structure (IRIS) and the spacecraft bus are collectively called the observatory. Jet Propulsion Laboratories and ISRO are implementing an observatory that will not only meet the respective national needs, but will also supply the scientific community with data to stimulate studies on surface deformation measurements through the repeated-pass InSAR technique. (Source – ISRO)
Know more : https://www.isro.gov.in/FutureMissions.html#
SPADEX
SPADEX (Space Docking Experiment) is an Indian technology mission to demonstrate autonomous docking. This project will develop and demonstrate the technologies required to dock two spacecraft (Chaser and Target) and to control one spacecraft from the Attitude Control System of another spacecraft while docked. Once docked, the Chaser and Target will be separated to conduct their designated payload experiments. This technology will be a precursor to future planetary missions including crew transfer, international participation, etc.

Also Read : 6 Best Certification Courses for 2024
AS Milkyway
Explore the galaxies of blogs with us.

